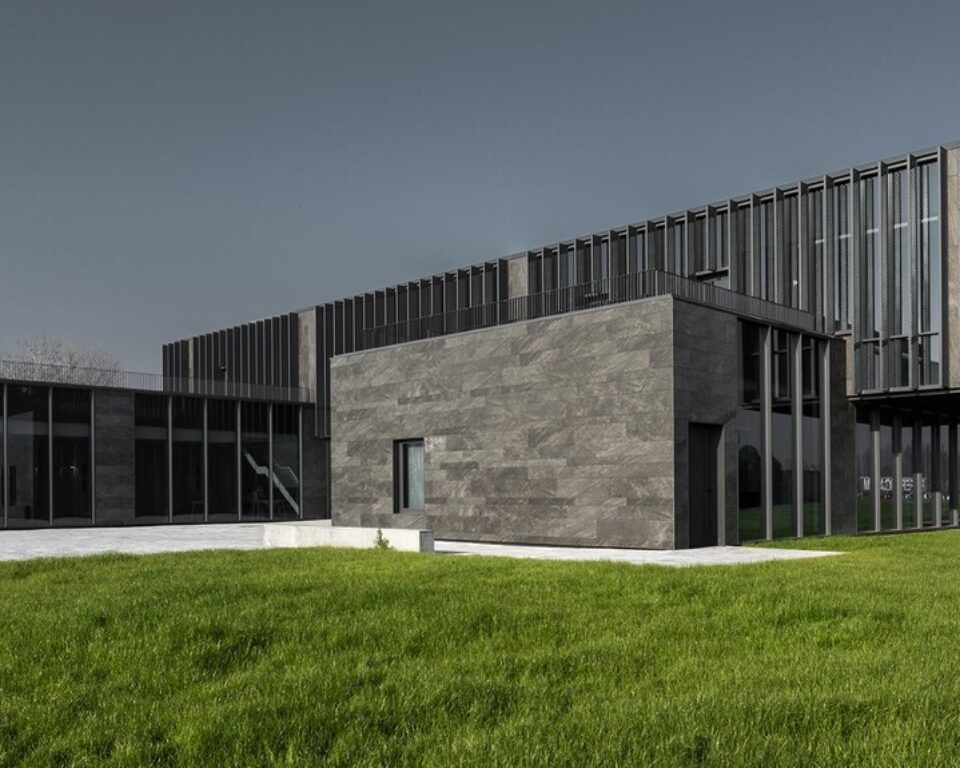
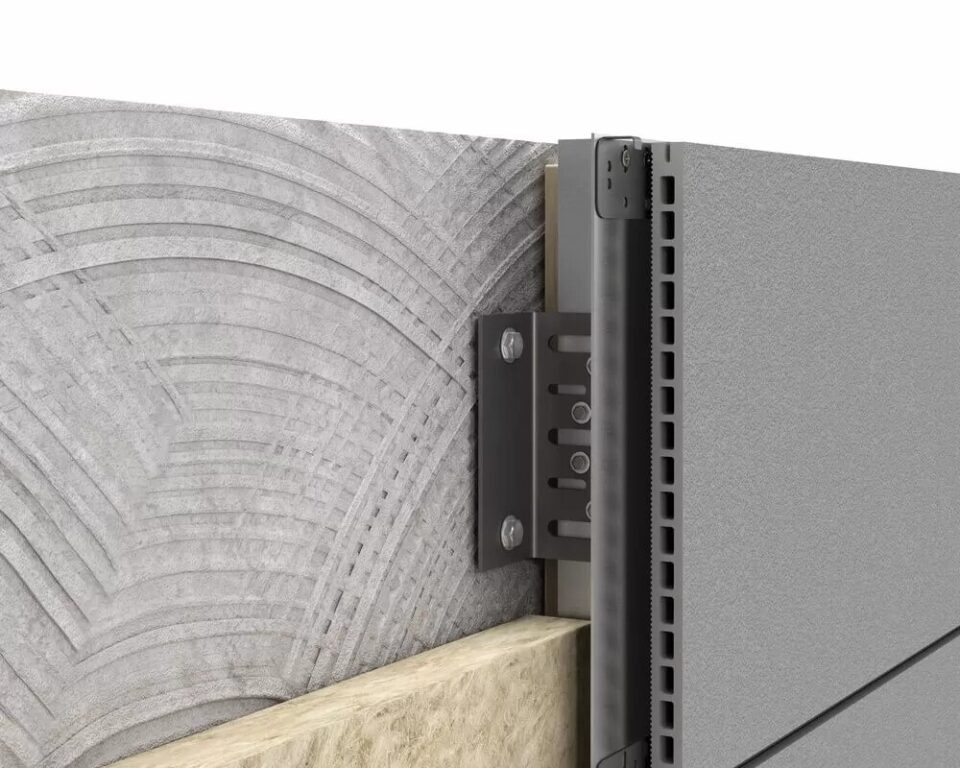
What is a ventilated facade?
A ventilated facade is an enclosure construction solution with a ventilated cavity between the exterior wall tiling panels and the support or interior partition walls.
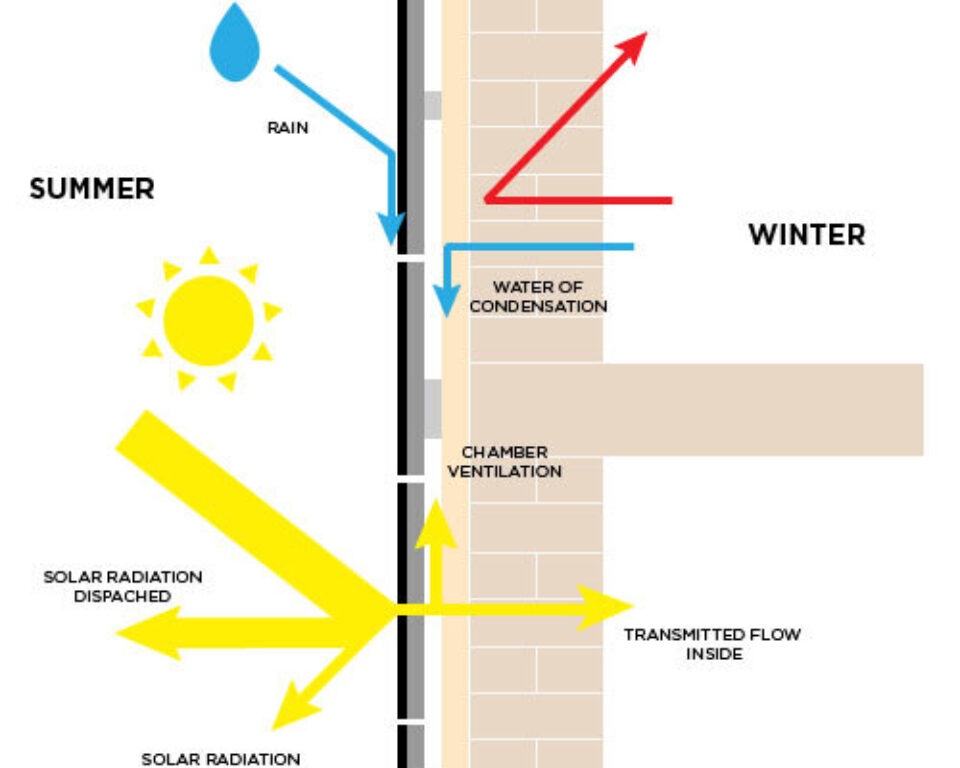
The ventilated cavity allows the exit and entry of air through its openings (bottom and top) as well as between the panel open joints.
The origin of ventilated facade systems arises from the need to protect structures from snow and rain. It’s a double-layer system formed by two enclosure leaves with a separation between to create a cavity allowing the circulation of an air flow that eliminates any type of humidity.
Why use the exa | TECH | FVH system?The exa-TECH FVH ventilated facade system is a set of elements that form a self-supporting substructure that is solidly attached to the support where it is installed. The slotted exa-TECH FVH panels are used to cover facades using this system.
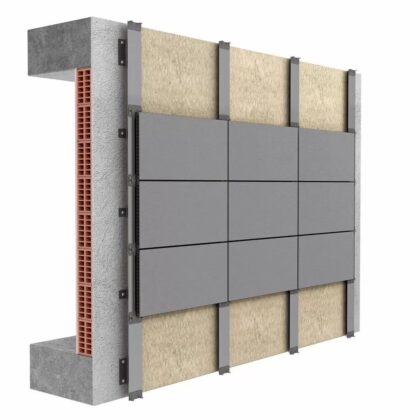





Characteristics of ventilated facades
Sustainable architecture, promoting energy efficiency and the utilization of environmentally-friendly materials, is increasingly prevalent. Ventilated facades, with their distinct features and fundamental elements, offer significant advantages in terms of insulation and energy conservation. The basic characteristics and elements of a ventilated facade include:
- Base Material: The underlying support structure to which the ventilated facade system is affixed, distinct from the facade system itself.
- Thermal Insulation: Installed over the backing wall to enhance thermal and acoustic performance, while eliminating thermal bridges.
- Ventilated Cavity: With a minimum gap of 20 mm, allowing for the diffusion of water that may enter due to rain or moisture from within the building.
- Substructure:
- Anchors: Fastening elements connecting the system to the backing wall to transmit loads.
- Brackets: Substructure components separating the cladding from the backing wall.
- Profiles: Longitudinal elements attached to the brackets, supporting the facade panels.
- Fixing System: Elements securing and holding the exterior cladding to the profiles.
- Cladding Panels: The external layer of the facade, constituting its visible surface.
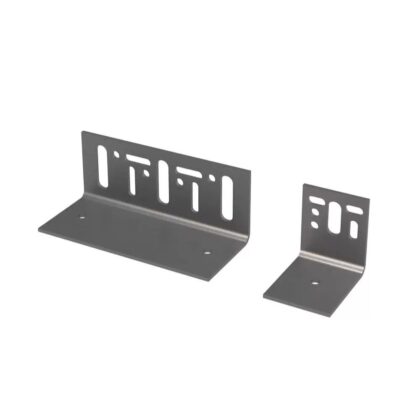
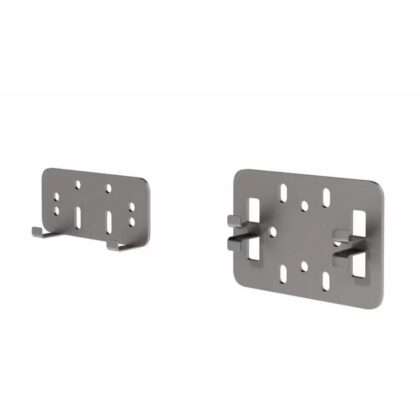
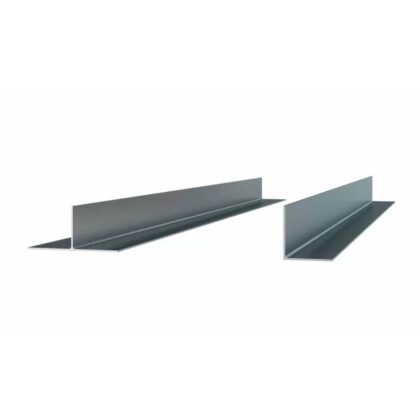
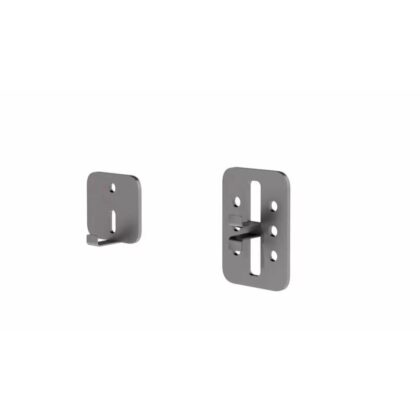




HOW IT WORKS
The UNI 11018 standards define the ventilated façade as a type of rain screen barrier where the cavity between the siding and the wall is designed in such a way that the air within it can flow naturally thanks to the principal called “chimney effect”, which notably improves the overall thermal-energy performance of the building.
© 2026 Emporio Ceramico | Tous droits réservés | Privacy policy
site web: matuvu.nu